rnn-time-to-event
(in construction)
An approximation of Recurrent Neural Networks to predict the Time to an Event
Notebook
Predictive Maintenance for the Turbofan Engine Dataset
Data Preparation
import keras
import keras.backend as K
print "Keras version", keras.__version__
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Setting seed for reproducibility
SEED = 42
np.random.seed(SEED)
Using TensorFlow backend.
Keras version 2.1.6
!mkdir Dataset
!mkdir Models
!wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Manelmc/rnn-time-to-event/master/Dataset/PM_test.txt -O Dataset/PM_test.txt
!wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Manelmc/rnn-time-to-event/master/Dataset/PM_train.txt -O Dataset/PM_train.txt
!wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Manelmc/rnn-time-to-event/master/Dataset/PM_truth.txt -O Dataset/PM_truth.txt
!ls Dataset
PM_test.txt PM_train.txt PM_truth.txt
Turbofan Train Set
from sklearn import preprocessing
# read training data - It is the aircraft engine run-to-failure data.
train_df = pd.read_csv('Dataset/PM_train.txt', sep=" ", header=None)
train_df.drop(train_df.columns[[26, 27]], axis=1, inplace=True)
train_df.columns = ['id', 'cycle', 'setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 's1', 's2', 's3',
's4', 's5', 's6', 's7', 's8', 's9', 's10', 's11', 's12', 's13', 's14',
's15', 's16', 's17', 's18', 's19', 's20', 's21']
train_df = train_df.sort_values(['id','cycle'])
# Data Labeling - generate column RUL (Remaining Useful Life or Time to Failure)
rul = pd.DataFrame(train_df.groupby('id')['cycle'].max()).reset_index()
rul.columns = ['id', 'max']
train_df = train_df.merge(rul, on=['id'], how='left')
train_df['RUL'] = train_df['max'] - train_df['cycle']
train_df.drop('max', axis=1, inplace=True)
# MinMax normalization (from 0 to 1)
train_df['cycle_norm'] = train_df['cycle']
cols_normalize = train_df.columns.difference(['id','cycle','RUL','label1','label2'])
min_max_scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
norm_train_df = pd.DataFrame(min_max_scaler.fit_transform(train_df[cols_normalize]),
columns=cols_normalize,
index=train_df.index)
join_df = train_df[train_df.columns.difference(cols_normalize)].join(norm_train_df)
train_df = join_df.reindex(columns = train_df.columns)
train_df[train_df["id"] == 1].tail()
| id | cycle | setting1 | setting2 | setting3 | s1 | s2 | s3 | s4 | s5 | ... | s14 | s15 | s16 | s17 | s18 | s19 | s20 | s21 | RUL | cycle_norm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 187 | 1 | 188 | 0.114943 | 0.750000 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.765060 | 0.683235 | 0.684166 | 0.0 | ... | 0.091599 | 0.753367 | 0.0 | 0.666667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.286822 | 0.089202 | 4 | 0.518006 |
| 188 | 1 | 189 | 0.465517 | 0.666667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.894578 | 0.547853 | 0.772451 | 0.0 | ... | 0.090670 | 0.744132 | 0.0 | 0.583333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.263566 | 0.301712 | 3 | 0.520776 |
| 189 | 1 | 190 | 0.344828 | 0.583333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.731928 | 0.614345 | 0.737677 | 0.0 | ... | 0.065229 | 0.759523 | 0.0 | 0.833333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.271318 | 0.239299 | 2 | 0.523546 |
| 190 | 1 | 191 | 0.500000 | 0.166667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.641566 | 0.682799 | 0.734639 | 0.0 | ... | 0.075704 | 0.740669 | 0.0 | 0.500000 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.240310 | 0.324910 | 1 | 0.526316 |
| 191 | 1 | 192 | 0.551724 | 0.500000 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.701807 | 0.662089 | 0.758778 | 0.0 | ... | 0.056714 | 0.717199 | 0.0 | 0.666667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.263566 | 0.097625 | 0 | 0.529086 |
5 rows × 28 columns
Turbofan Test Set
from sklearn import preprocessing
# read test data - It is the aircraft engine operating data without failure events recorded.
test_df = pd.read_csv('Dataset/PM_test.txt', sep=" ", header=None)
test_df.drop(test_df.columns[[26, 27]], axis=1, inplace=True)
test_df.columns = ['id', 'cycle', 'setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 's1', 's2', 's3',
's4', 's5', 's6', 's7', 's8', 's9', 's10', 's11', 's12', 's13', 's14',
's15', 's16', 's17', 's18', 's19', 's20', 's21']
# MinMax normalization (from 0 to 1)
test_df['cycle_norm'] = test_df['cycle']
norm_test_df = pd.DataFrame(min_max_scaler.transform(test_df[cols_normalize]),
columns=cols_normalize,
index=test_df.index)
test_join_df = test_df[test_df.columns.difference(cols_normalize)].join(norm_test_df)
test_df = test_join_df.reindex(columns = test_df.columns)
test_df = test_df.reset_index(drop=True)
# read ground truth data - It contains the information of true remaining cycles for each engine in the testing data.
truth_df = pd.read_csv('Dataset/PM_truth.txt', sep=" ", header=None)
truth_df.drop(truth_df.columns[[1]], axis=1, inplace=True)
# generate column max for test data
rul = pd.DataFrame(test_df.groupby('id')['cycle'].max()).reset_index()
rul.columns = ['id', 'max']
truth_df.columns = ['more']
truth_df['id'] = truth_df.index + 1
truth_df['max'] = rul['max'] + truth_df['more']
truth_df.drop('more', axis=1, inplace=True)
# generate RUL for test data
test_df = test_df.merge(truth_df, on=['id'], how='left')
test_df['RUL'] = test_df['max'] - test_df['cycle']
test_df.drop('max', axis=1, inplace=True)
test_df[test_df["id"] == 1].tail()
| id | cycle | setting1 | setting2 | setting3 | s1 | s2 | s3 | s4 | s5 | ... | s14 | s15 | s16 | s17 | s18 | s19 | s20 | s21 | cycle_norm | RUL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | 1 | 27 | 0.459770 | 0.583333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.262048 | 0.340310 | 0.304862 | 0.0 | ... | 0.140881 | 0.479030 | 0.0 | 0.333333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.565891 | 0.688898 | 0.072022 | 116 |
| 27 | 1 | 28 | 0.626437 | 0.916667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.216867 | 0.505995 | 0.321404 | 0.0 | ... | 0.180359 | 0.469796 | 0.0 | 0.333333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.534884 | 0.629660 | 0.074792 | 115 |
| 28 | 1 | 29 | 0.580460 | 0.583333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.222892 | 0.351210 | 0.267725 | 0.0 | ... | 0.171277 | 0.370527 | 0.0 | 0.333333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.682171 | 0.646092 | 0.077562 | 114 |
| 29 | 1 | 30 | 0.356322 | 0.833333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.475904 | 0.320035 | 0.316003 | 0.0 | ... | 0.179843 | 0.331281 | 0.0 | 0.250000 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.736434 | 0.707954 | 0.080332 | 113 |
| 30 | 1 | 31 | 0.465517 | 0.833333 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.412651 | 0.221932 | 0.281229 | 0.0 | ... | 0.155692 | 0.298192 | 0.0 | 0.416667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.519380 | 0.636564 | 0.083102 | 112 |
5 rows × 28 columns
Apply right padding to all the sequences
def pad_sequence(df, max_seq_length, mask=0):
"""
Applies right padding to a sequences until max_seq_length with mask
"""
return np.pad(df.values, ((0, max_seq_length - df.values.shape[0]), (0,0)),
"constant", constant_values=mask)
def pad_engines(df, cols, max_batch_len, mask=0):
"""
Applies right padding to the columns "cols" of all the engines
"""
return np.array([pad_sequence(df[df['id'] == batch_id][cols], max_batch_len, mask=mask)
for batch_id in df['id'].unique()])
max_batch_len = train_df['id'].value_counts().max()
train_cols = ['s' + str(i) for i in range(1,22)] + ['setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 'cycle_norm']
test_cols = ["RUL"]
X = pad_engines(train_df, train_cols, max_batch_len)
Y = pad_engines(train_df, test_cols, max_batch_len)
Split into train, validation and test
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Split into train and validation
train_X, val_X, train_Y, val_Y = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.20, random_state=SEED)
# Test set from CMAPSS
test_X = pad_engines(test_df, train_cols, max_batch_len)
test_Y = pad_engines(test_df, test_cols, max_batch_len)
# In the WTTE-RNN architecture we will predict 2 parameters (alpha and beta)
# alpha is initialised to 1
train_Y_wtte = np.concatenate((train_Y, np.ones(train_Y.shape)), axis=2)
val_Y_wtte = np.concatenate((val_Y, np.ones(val_Y.shape)), axis=2)
test_Y_wtte = np.concatenate((test_Y, np.ones(test_Y.shape)), axis=2)
print "Train:\n", " X:", train_X.shape, "\n Y:", train_Y.shape, "\n Y_wtte:", train_Y_wtte.shape
print "\nValidation:\n", " X:", val_X.shape, "\n Y:", val_Y.shape, "\n Y_wtte:", val_Y_wtte.shape
print "\nTest:\n", " X:", test_X.shape, "\n Y:", test_Y.shape, "\n Y_wtte:", test_Y_wtte.shape
Train:
X: (80, 362, 25)
Y: (80, 362, 1)
Y_wtte: (80, 362, 2)
Validation:
X: (20, 362, 25)
Y: (20, 362, 1)
Y_wtte: (20, 362, 2)
Test:
X: (100, 362, 25)
Y: (100, 362, 1)
Y_wtte: (100, 362, 2)
Baseline
from keras.layers import Masking
from keras.layers.core import Activation
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, LSTM, TimeDistributed
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
# Model path
baseline_path = "baseline_model"
# Callbacks
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=30,
verbose=0,
mode='min')
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(baseline_path,
monitor='val_loss',
save_best_only=True,
mode='min',
verbose=0)
# dimensions of the model
nb_features = train_X.shape[2]
nb_out = train_Y.shape[2]
model = Sequential()
# Masking layer so the right padding is ignored
# at each layer of the network
model.add(Masking(mask_value=0.,
input_shape=(max_batch_len, nb_features)))
# Then there s an LSTM layer with 100 units
# Recurrent Dropout is also applied after each
# LSTM layer to control overfitting.
model.add(LSTM(
units=100,
recurrent_dropout=0.2,
return_sequences=True))
# followed by another LSTM layer with 50 units
model.add(LSTM(
units=50,
recurrent_dropout=0.2,
return_sequences=True))
# Final layer is a Time-Distributed Dense layer
# with a single unit with an Exponential activation
model.add(TimeDistributed(Dense(nb_out, activation=K.exp)))
model.compile(loss="mse", optimizer=keras.optimizers.RMSprop())
print(model.summary())
# fit the network
history = model.fit(train_X, train_Y, epochs=500, batch_size=16,
validation_data=(val_X, val_Y), shuffle=True,
verbose=2, callbacks = [early_stopping, checkpoint])
# list all data in history
print(history.history.keys())
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
masking_1 (Masking) (None, 362, 25) 0
_________________________________________________________________
lstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 362, 100) 50400
_________________________________________________________________
lstm_2 (LSTM) (None, 362, 50) 30200
_________________________________________________________________
time_distributed_1 (TimeDist (None, 362, 1) 51
=================================================================
Total params: 80,651
Trainable params: 80,651
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
...
- 14s - loss: 1145.8300 - val_loss: 684.7579
Epoch 309/500
- 15s - loss: 1483.2823 - val_loss: 665.0914
Epoch 310/500
- 15s - loss: 1484.7324 - val_loss: 676.9185
Epoch 311/500
- 15s - loss: 1204.1237 - val_loss: 621.4485
Epoch 312/500
- 15s - loss: 1293.4628 - val_loss: 611.2367
Epoch 313/500
- 15s - loss: 1410.6540 - val_loss: 599.2881
Epoch 314/500
- 15s - loss: 1280.4136 - val_loss: 651.2672
Epoch 315/500
- 15s - loss: 1233.0307 - val_loss: 634.8255
Epoch 316/500
- 15s - loss: 1339.8630 - val_loss: 702.0963
Epoch 317/500
- 14s - loss: 1249.2757 - val_loss: 789.5427
Epoch 318/500
- 15s - loss: 1364.1424 - val_loss: 834.3046
['loss', 'val_loss']
# Execute if training in Colaboratory (preferably from Chrome)
# Downloads the model after the training finishes
from google.colab import files
files.download(baseline_path)
# Move the model to the expected folder
!mv baseline_path Models/
# Validation loss vs the Training loss
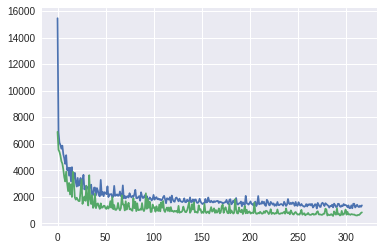
%matplotlib inline
plt.plot(history.history["loss"])
plt.plot(history.history["val_loss"])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f6039681c50>]
# Execute if you want to upload a model to Collaboratory
from google.colab import files
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(
name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
<input type="file" id="files-f6e556f7-746f-4e94-b68a-9859a114544e" name="files[]" multiple disabled />
<output id="result-f6e556f7-746f-4e94-b68a-9859a114544e">
Upload widget is only available when the cell has been executed in the
current browser session. Please rerun this cell to enable.
</output>
<script src="/nbextensions/google.colab/files.js"></script>
from keras.models import load_model
# It's important to load the model after the training
# The keras Checkpoint will save the best model in terms
# of the validation loss in the specified path
model = load_model("Models/" + baseline_path, custom_objects={"exp": K.exp})
%matplotlib inline
from math import sqrt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score
# We save the validation errors to later compare the models
validation_baseline = model.predict(val_X).flatten()
def evaluate_and_plot(model, evaluation_data, weibull_function=None):
"""
Generate scores dataframe and plot the RUL
"""
fig = plt.figure()
i = 1
score_df = pd.DataFrame({"Method": ["MAE", "RMSE", "R2"]})
for name_set, train_set, test_set in evaluation_data:
if weibull_function is None:
y_pred = model.predict(train_set).flatten()
else:
y_pred = [weibull_function(alpha, beta)
for batch in model.predict(train_set)
for beta, alpha in batch]
l = test_set[:,:,0].flatten()
# To validate we remove the right padding
y_true = np.ma.compressed(np.ma.masked_where(l==0, l))
y_pred = np.ma.compressed(np.ma.masked_where(l==0, y_pred))
score_mae = "{0:.2f}".format(mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred))
score_rmse = "{0:.2f}".format(sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)))
score_r2 = "{0:.3f}".format(r2_score(y_true, y_pred))
score_df[name_set] = [score_mae, score_rmse, score_r2]
ax = fig.add_subplot(6, 1, i)
ax.title.set_text(name_set)
ax.title.set_fontsize(20)
i += 1
plt.plot(y_pred[0:2500])
plt.plot(y_true[0:2500])
ax = fig.add_subplot(6, 1, i)
i += 1
plt.plot(y_pred[2500:5000])
plt.plot(y_true[2500:5000])
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.45)
fig.set_size_inches(15, i*2.2)
return score_df.T
evaluate_and_plot(model,
[("Train", train_X, train_Y),
("Validation", val_X, val_Y),
("Test", test_X, test_Y)])
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
| Train | 21.19 | 33.57 | 0.766 |
| Validation | 17.36 | 23.98 | 0.866 |
| Test | 27.03 | 37.41 | 0.598 |

Adapting to WTTE-RNN
# Install wtte package from Martinsson
!pip install wtte
Collecting wtte
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/95/0e/8affc53f47d4ceb69fc80484fd87ad886c6cab7f4ce0add38076b6092d76/wtte-1.1.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Requirement already satisfied: scipy in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from wtte) (0.19.1)
Requirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from wtte) (1.14.5)
Requirement already satisfied: keras>=2.0 in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from wtte) (2.1.6)
Requirement already satisfied: pandas in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from wtte) (0.22.0)
Collecting six==1.10.0 (from wtte)
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/c8/0a/b6723e1bc4c516cb687841499455a8505b44607ab535be01091c0f24f079/six-1.10.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Requirement already satisfied: pyyaml in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from keras>=2.0->wtte) (3.13)
Requirement already satisfied: h5py in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from keras>=2.0->wtte) (2.8.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pytz>=2011k in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from pandas->wtte) (2018.5)
Requirement already satisfied: python-dateutil in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from pandas->wtte) (2.5.3)
Installing collected packages: six, wtte
Found existing installation: six 1.11.0
Uninstalling six-1.11.0:
Successfully uninstalled six-1.11.0
Successfully installed six-1.10.0 wtte-1.1.1
# Loss and activation functions from Martinsson
# These are not used in the final version because
# the wtte package has useful regularization tools
def weibull_loglik_discrete(y_true, y_pred, epsilon=K.epsilon()):
y = y_true[..., 0]
u = y_true[..., 1]
a = y_pred[..., 0]
b = y_pred[..., 1]
hazard0 = K.pow((y + epsilon) / a, b)
hazard1 = K.pow((y + 1.0) / a, b)
loss = u * K.log(K.exp(hazard1 - hazard0) - (1.0 - epsilon)) - hazard1
return -loss
def activation_weibull(y_true):
a = y_true[..., 0]
b = y_true[..., 1]
a = K.exp(a)
b = K.sigmoid(b)
return K.stack([a, b], axis=-1)
from keras.layers import Masking
from keras.layers.core import Activation
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, LSTM, TimeDistributed, Lambda
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, TerminateOnNaN, ModelCheckpoint
import wtte.weibull as weibull
import wtte.wtte as wtte
# Since we use a lambda in the last layer the model
# is not saved well in keras, instead we save the weights.
# This requires compiling the model to load the weights
baseline_wtte_path = "baseline_wtte_model_weights"
# Callbacks
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=30,
verbose=0,
mode='min')
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(baseline_wtte_path,
monitor='val_loss',
save_best_only=True,
save_weights_only=True,
mode='min',
verbose=0)
nb_features = train_X.shape[2]
nb_out = train_Y.shape[1]
model = Sequential()
model.add(Masking(mask_value=0.,
input_shape=(max_batch_len, nb_features)))
model.add(LSTM(
input_shape=(None, nb_features),
units=100,
recurrent_dropout=0.2,
return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(
units=50,
recurrent_dropout=0.2,
return_sequences=True))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Dense(2)))
# uncomment this line and comment the next to use
# activation_weibull function:
# model.add(Activation(activation_weibull))
model.add(Lambda(wtte.output_lambda,
arguments={# Initialization value around it's scale
"init_alpha": np.nanmean(train_Y_wtte[:,0]),
# Set a maximum
"max_beta_value": 10.0
},
))
# Same for the loss "weibull_loglik_discrete"
# model.compile(loss=weibull_loglik_discrete, optimizer='rmsprop')
# We use clipping on the loss
loss = wtte.Loss(kind='discrete', clip_prob=1e-5).loss_function
model.compile(loss=loss, optimizer='rmsprop')
print(model.summary())
# fit the network
history = model.fit(train_X, train_Y_wtte, epochs=500, batch_size=16,
validation_data=(val_X, val_Y_wtte), shuffle=True, verbose=2,
callbacks = [early_stopping, checkpoint, TerminateOnNaN()])
# list all data in history
print(history.history.keys())
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
masking_4 (Masking) (None, None, 25) 0
_________________________________________________________________
lstm_7 (LSTM) (None, None, 100) 50400
_________________________________________________________________
lstm_8 (LSTM) (None, None, 50) 30200
_________________________________________________________________
time_distributed_4 (TimeDist (None, None, 2) 102
_________________________________________________________________
lambda_2 (Lambda) (None, None, 2) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 80,702
Trainable params: 80,702
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
...
- 12s - loss: 2.5586 - val_loss: 2.4429
Epoch 353/500
- 13s - loss: 2.5923 - val_loss: 2.5299
Epoch 354/500
- 12s - loss: 2.6591 - val_loss: 2.4070
Epoch 355/500
- 12s - loss: 2.5594 - val_loss: 2.5139
Epoch 356/500
- 13s - loss: 2.5870 - val_loss: 2.4082
Epoch 357/500
- 12s - loss: 2.6275 - val_loss: 2.4218
['loss', 'val_loss']
# Execute if training in Colaboratory (preferably from Chrome)
# Downloads the model after the training finishes
from google.colab import files
files.download(baseline_wtte_path)
# Move the model to the expected folder
!mv baseline_wtte_path Models/
%matplotlib inline
plt.plot(history.history["loss"])
plt.plot(history.history["val_loss"])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f351865d990>]
# Execute if you want to upload a model to Collaboratory
from google.colab import files
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(
name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
<input type="file" id="files-8f58d2a2-d3f6-43fa-93dc-a6fbf59eed70" name="files[]" multiple disabled />
<output id="result-8f58d2a2-d3f6-43fa-93dc-a6fbf59eed70">
Upload widget is only available when the cell has been executed in the
current browser session. Please rerun this cell to enable.
</output>
<script src="/nbextensions/google.colab/files.js"></script>
Saving baseline_wtte_model_weights (1) to baseline_wtte_model_weights (1)
User uploaded file "baseline_wtte_model_weights (1)" with length 340528 bytes
# Compile model first to load weights
model.load_weights("Models/" + baseline_wtte_path)
Weibull Methods
$\mu = \beta\Gamma(1 + \alpha^{-1})$
$\sigma^2 = \beta^2[\Gamma(1 + 2\alpha^{-1}) - \Gamma^2(1 + \alpha^{-1})]$
$mode = \beta\frac{\alpha-1}{\alpha}^{1/\alpha}$
Inverse CDF $ = \beta (-\log(1 - x))^\frac{1}{\alpha} $ when $ 0<x<1 $
from math import gamma, log, sqrt
def mean_weibull(alpha, beta):
return beta*gamma(1 + 1./alpha)
def mode_weibull(alpha, beta):
return beta*((alpha-1)/alpha)**(1./alpha) if alpha > 1 else 0
def median_weibull(alpha, beta):
return beta*(log(2)**(1./alpha))
def var_weibull(alpha, beta):
return beta**2*(gamma(1 + 2./alpha) - gamma(1 + 1./alpha)**2)
def pdf_weibull(x, alpha, beta):
return (alpha/beta)*(x/beta)**(alpha - 1)*np.exp(-(x/beta)**alpha)
def inverse_cdf_weibull(x, alpha, beta):
return beta*np.power((-np.log(1.-x)), 1./alpha)
def survival_weibull(x, alpha, beta):
return np.e**-((x/beta)**alpha)
Mean, Mode and Median

%matplotlib inline
print "Mode"
print evaluate_and_plot(model,
[("Train", train_X, train_Y_wtte),
("Validation", val_X, val_Y_wtte),
("Test", test_X, test_Y_wtte)],
weibull_function = mode_weibull)
# comment the next line to visualise the plot for the mode
plt.close()
print "\nMedian"
print evaluate_and_plot(model,
[("Train", train_X, train_Y_wtte),
("Validation", val_X, val_Y_wtte),
("Test", test_X, test_Y_wtte)],
weibull_function = median_weibull)
# comment the next line to visualise the plot for the median
plt.close()
# We save the validation errors to later compare the models
validation_wtte = [mean_weibull(alpha, beta)
for batch in model.predict(val_X)
for beta, alpha in batch]
print "\nMean"
print evaluate_and_plot(model,
[("Train", train_X, train_Y_wtte),
("Validation", val_X, val_Y_wtte),
("Test", test_X, test_Y_wtte)],
weibull_function = mean_weibull)
Mode
0 1 2
Method MAE RMSE R2
Train 21.53 34.69 0.750
Validation 17.94 26.48 0.836
Test 27.46 38.59 0.572
Median
0 1 2
Method MAE RMSE R2
Train 21.05 33.51 0.767
Validation 17.79 25.48 0.848
Test 26.72 37.49 0.596
Mean
0 1 2
Method MAE RMSE R2
Train 20.94 33.14 0.772
Validation 17.79 25.26 0.851
Test 26.51 37.22 0.602

Evolution of the pdf through the cycles of an engine (PLOT)
import random
import seaborn as sns
random.seed(SEED)
lot = random.sample(train_X, 3)
random.seed(SEED)
lot += random.sample(val_X, 3)
random.seed(SEED)
lot += random.sample(test_X, 3)
palette = list(reversed(sns.color_palette("RdBu_r", 250)))
fig = plt.figure()
j = 1
for batch in lot:
size = batch[~np.all(batch == 0, axis=1)].shape[0]
y_pred_wtte = model.predict(batch.reshape(1, max_batch_len, nb_features))[0]
y_pred_wtte = y_pred_wtte[:size]
x = np.arange(1, 400.)
freq = 5
ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 3, j)
i=0
for beta, alpha in y_pred_wtte[0::freq][2:]:
mean = mode_weibull(alpha, beta)
color=palette[int(mean)] if i < len(palette) else palette[-1]
plt.plot(x, pdf_weibull(x, alpha, beta), color=color)
i += 1
ax.set_ylim([0, 0.07])
ax.set_xlim([0, 300])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
if j == 2:
ax.title.set_text("Train")
elif j == 5:
ax.title.set_text("Validation")
elif j == 8:
ax.title.set_text("Test")
j += 1
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.15, hspace=0.25)
fig.set_size_inches(10,10)
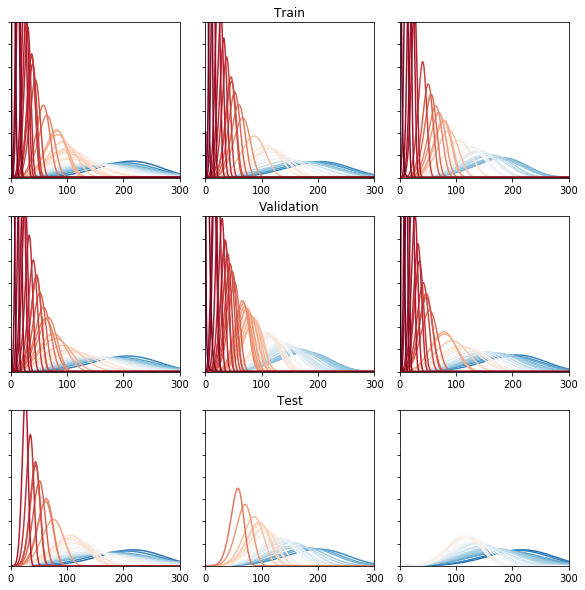
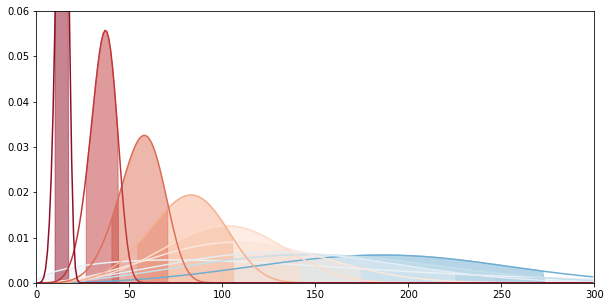
Confidence Interval of the Weibull Distribution
%matplotlib inline
from scipy.stats import dweibull
batch = lot[0]
size = batch[~np.all(batch == 0, axis=1)].shape[0]
y_pred_wtte = model.predict(batch.reshape(1, max_batch_len, nb_features))[0]
y_pred_wtte = y_pred_wtte[:size]
fig = plt.figure()
fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
for beta, alpha in y_pred_wtte[0::20]:
x = np.arange(1, 300.)
mean = mean_weibull(alpha, beta)
sigma = np.sqrt(var_weibull(alpha, beta))
plt.plot(x, pdf_weibull(x, alpha, beta), color=palette[int(mean)])
# alpha is the shape parameter
conf = dweibull.interval(0.95, alpha, loc=mean, scale=sigma)
plt.fill([conf[0]] + list(np.arange(conf[0], conf[1])) + [conf[1]],
[0] + list(pdf_weibull(np.arange(conf[0], conf[1]), alpha, beta)) + [0],
color=palette[int(mean)], alpha=0.5)
axes = plt.gca()
axes.set_ylim([0., 0.06])
axes.set_xlim([0., 300.])
fig.set_size_inches(10,5)
/anaconda2/envs/ALL_BF/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:16: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in power
app.launch_new_instance()
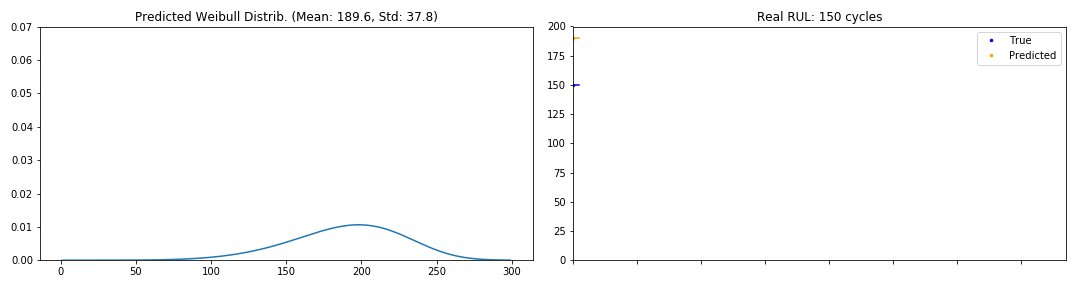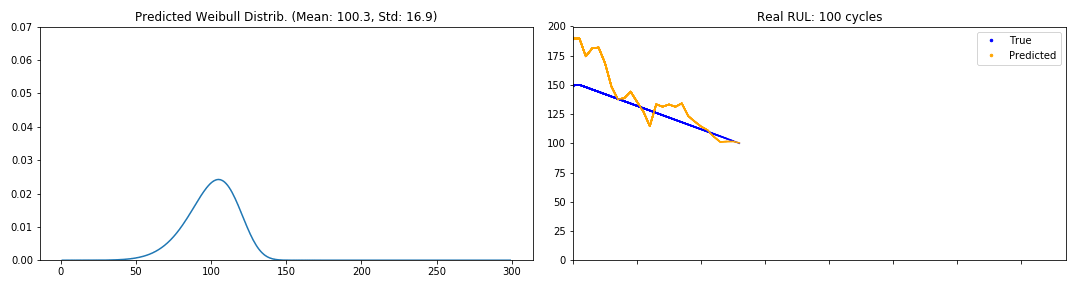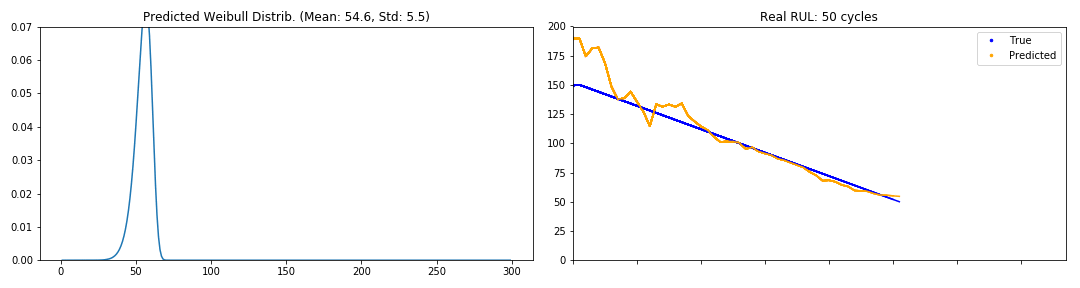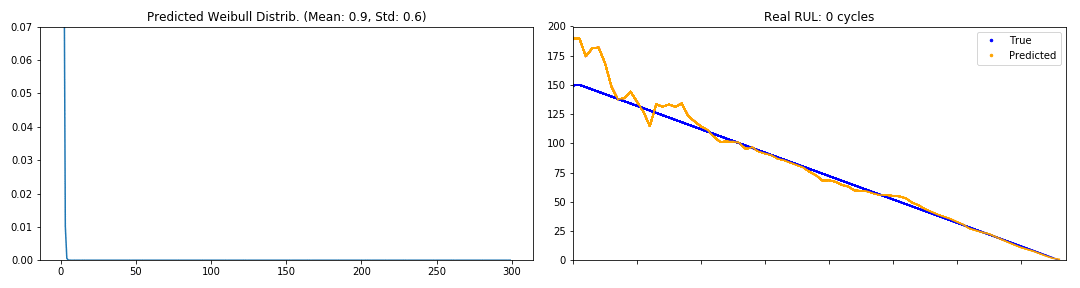
Evolution of the pdf through the cycles of an engine (GIFs)
import sys
import random
from math import gamma
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
from scipy.stats import dweibull
def generate_gif(y_pred, y_true, path, freq=2):
# remove mask if exists
y_true = y_true[y_true != 0]
y_pred = y_pred[:y_true.shape[0]]
frames = zip(y_true, y_pred)
# pad, w_pad, h_pad, and rect
fig = plt.figure()
global ax1, ax2
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,2)
fig.set_tight_layout(True)
x = np.arange(1, 300.)
beta, alpha = y_pred[0]
line1, = ax1.plot(x, pdf_weibull(x, alpha, beta))
global i, acc_y_true, acc_y_pred
i = 0
predict_mean = mean_weibull(alpha, beta)
ax2.plot(i, y_true[0], 'bo', label="True", ms=2.5)
ax2.plot(i, predict_mean, 'o', color="orange", label="Predicted", ms=2.5)
ax2.legend(loc="upper right")
# limits
ax1.set_ylim([0, 0.07])
ax2.set_ylim([0, y_true[0] + 10])
ax2.set_xlim([0, len(frames)/freq + 2])
ax2.set_xticklabels([])
# acc values
acc_y_true = []
acc_y_pred = []
def update(instant):
y_true_t, y_pred_t = instant
beta, alpha = y_pred_t
# print y_true
pdf = pdf_weibull(x, alpha, beta)
line1.set_ydata(pdf)
global i, acc_y_true, acc_y_pred
i += 1
mean = mean_weibull(alpha, beta)
sigma = np.sqrt(var_weibull(alpha, beta))
acc_y_pred += [mean]
acc_y_true += [y_true_t]
ax2.plot(range(len(acc_y_true)), acc_y_true, 'b', label="True")
ax2.plot(range(len(acc_y_pred)), acc_y_pred, color="orange", label="Predicted")
conf = dweibull.interval(0.95, alpha, loc=mean, scale=sigma)
ax1.set_title("PDF Weibull Distrib. (Mean: " + "{0:.1f}".format(mean)
+ ", Std: " + "{0:.1f}".format(sigma) + ")"
+ " CI 95%: [{0:.1f}, {1:.1f}]".format(*conf))
ax2.set_title("Real RUL: " + str(y_true_t) + " cycles")
fig.set_size_inches(15,4)
anim = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=frames[0::freq])
anim.save(path, writer="imagemagick")
plt.close()
random.seed(SEED)
batch_X, batch_Y = random.choice(zip(train_X, train_Y))
y_pred_wtte = model.predict(batch_X.reshape(1, max_batch_len, nb_features))[0]
gif_path = "Images/train_engine_sample.gif"
generate_gif(y_pred_wtte, batch_Y, gif_path, freq=2)
print "Train Sample"
from IPython.display import HTML
HTML('<img src="'+ gif_path + '">')
Train Sample

random.seed(SEED)
batch_X, batch_Y = random.choice(zip(val_X, val_Y))
y_pred_wtte = model.predict(batch_X.reshape(1, max_batch_len, nb_features))[0]
gif_path = "Images/val_engine_sample.gif"
generate_gif(y_pred_wtte, batch_Y, gif_path, freq=2)
print "Validation Sample"
from IPython.display import HTML
HTML('<img src="'+ gif_path + '">')
Validation Sample

random.seed(SEED)
batch_X, batch_Y = random.choice(zip(test_X, test_Y))
y_pred_wtte = model.predict(batch_X.reshape(1, max_batch_len, nb_features))[0]
gif_path = "Images/test_engine_sample.gif"
generate_gif(y_pred_wtte, batch_Y, gif_path, freq=2)
print "Test Sample"
from IPython.display import HTML
HTML('<img src="'+ gif_path + '">')
Test Sample

GRU variant
from keras.layers import Masking
from keras.layers.core import Activation
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, GRU, TimeDistributed, Lambda
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, TerminateOnNaN, ModelCheckpoint
import wtte.weibull as weibull
import wtte.wtte as wtte
baseline_gru_path = "baseline_gru_model_weights"
# Callbacks
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=30,
verbose=0,
mode='min')
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(baseline_gru_path,
monitor='val_loss',
save_best_only=True,
save_weights_only=True,
mode='min',
verbose=0)
nb_features = train_X.shape[2]
nb_out = train_Y.shape[1]
init_alpha = np.nanmean(train_Y_wtte[:,0])
model = Sequential()
model.add(Masking(mask_value=0.,
input_shape=(max_batch_len, nb_features)))
# We substitute LSTM for GRU
model.add(GRU(
input_shape=(None, nb_features),
units=100,
recurrent_dropout=0.2,
return_sequences=True))
model.add(GRU(
units=50,
recurrent_dropout=0.2,
return_sequences=True))
model.add(TimeDistributed(Dense(2)))
model.add(Lambda(wtte.output_lambda,
arguments={# Initialization value around it's scale
"init_alpha": np.nanmean(train_Y_wtte[:,0]),
# Set a maximum
"max_beta_value": 10.0,
# We set the scalefactor to avoid exploding gradients
"scalefactor": 0.25
},
))
loss = wtte.Loss(kind='discrete', clip_prob=1e-5).loss_function
model.compile(loss=loss, optimizer='rmsprop')
print(model.summary())
# fit the network
history = model.fit(train_X, train_Y_wtte, epochs=500, batch_size=16,
validation_data=(val_X, val_Y_wtte), shuffle=True, verbose=2,
callbacks = [early_stopping, checkpoint, TerminateOnNaN()])
# list all data in history
print(history.history.keys())
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
masking_6 (Masking) (None, None, 25) 0
_________________________________________________________________
gru_6 (GRU) (None, None, 100) 37800
_________________________________________________________________
gru_7 (GRU) (None, None, 50) 22650
_________________________________________________________________
time_distributed_5 (TimeDist (None, None, 2) 102
_________________________________________________________________
lambda_5 (Lambda) (None, None, 2) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 60,552
Trainable params: 60,552
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
...
Epoch 379/500
- 4s - loss: 2.5791 - val_loss: 2.4811
Epoch 380/500
- 4s - loss: 2.4674 - val_loss: 2.3694
Epoch 381/500
- 4s - loss: 2.4272 - val_loss: 2.3636
Epoch 382/500
- 4s - loss: 2.4483 - val_loss: 2.4244
Epoch 383/500
- 4s - loss: 2.4518 - val_loss: 2.4219
Epoch 384/500
- 4s - loss: 2.4448 - val_loss: 2.3649
Epoch 385/500
- 4s - loss: 2.5142 - val_loss: 2.3681
Epoch 386/500
- 4s - loss: 2.4157 - val_loss: 2.4423
['loss', 'val_loss']
# Execute if training in Colaboratory (preferably from Chrome)
# Downloads the model after the training finishes
from google.colab import files
files.download(baseline_gru_path)
# Move the model to the expected folder
!mv baseline_gru_path Models/
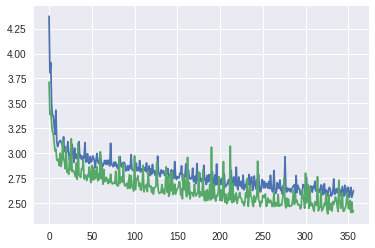
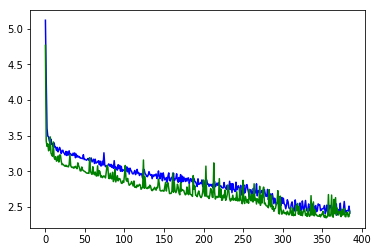
%matplotlib inline
plt.plot(history.history["loss"], color="blue")
plt.plot(history.history["val_loss"], color="green")
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1a353fcf10>]
# Execute if you want to upload a model to Collaboratory
from google.colab import files
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(
name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
# Compile model first to load weights
model.load_weights("Models/" + baseline_gru_path)
# We save the validation errors to later compare the models
validation_gru = [mean_weibull(alpha, beta)
for batch in model.predict(val_X)
for beta, alpha in batch]
evaluate_and_plot(model,
[("Train", train_X, train_Y_wtte),
("Validation", val_X, val_Y_wtte),
("Test", test_X, test_Y_wtte)],
weibull_function = mean_weibull)
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
| Train | 20.94 | 33.14 | 0.772 |
| Validation | 17.79 | 25.26 | 0.851 |
| Test | 26.51 | 37.22 | 0.602 |

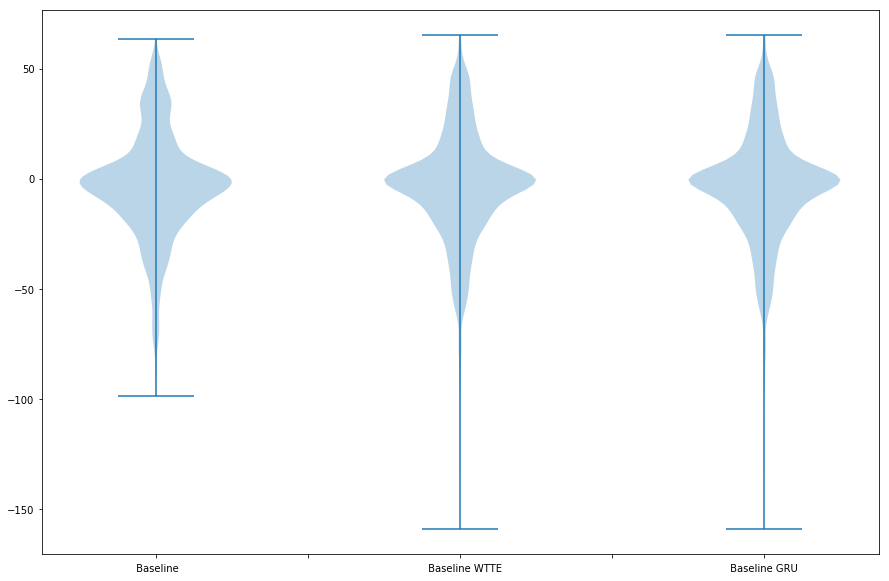
Result
The are three models:
- baseline
- baseline WTTE-RNN LSTM
- baseline WTTE-RNN GRU
The mean is used as the expected value of the RUL.
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns
l = val_Y.flatten()
y_true = np.ma.compressed(np.ma.masked_where(l==0, l))
y_pred_baseline = np.ma.compressed(np.ma.masked_where(l==0, validation_baseline))
y_pred_wtte = np.ma.compressed(np.ma.masked_where(l==0, validation_wtte))
y_pred_gru = np.ma.compressed(np.ma.masked_where(l==0, validation_gru))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.violinplot([y_pred_baseline - y_true,
y_pred_wtte - y_true,
y_pred_gru - y_true])
ax.set_xticklabels([])
plt.figtext(0.21, 0.1, ' Baseline')
plt.figtext(0.480, 0.1, ' Baseline WTTE')
plt.figtext(0.76, 0.1, ' Baseline GRU')
fig.set_size_inches(15, 10)